Noise Cleaning: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Before Noisecleaning == |
|||
Before doing any processing on your file, '''do''' export a copy of your file in FLAC format (click File | Export Audio and select FLAC files from the 'Save as type' drop-down menu). Then if anything goes wrong, you have a raw lossless copy that you can import back into Audacity. |
|||
== Noisecleaning == |
== Noisecleaning == |
||
In Librivox files, Noise Removal works by removing or reducing the amount of "noise" between the speaking portions of our recordings. Whichever program is being used, the concept is the same. The program must be told what the "noise" is to be defined as (that's your job), and then the program diminishes the "noise" that it finds within the file, to the degree that you tell it to do so. You can change the settings so that the program diminishes the noise very aggressively, or very lightly. |
|||
There are some simple but important points to remember before you start Noise Removal. |
|||
:* Leave some "room silence" at the end of your recording where everything is as quiet as possible. This is what you will use to tell the program what "noise" is. |
|||
:* It's better to run light Noise Removal twice than to do it aggressively once. |
|||
:* Always listen to the file after you've done the Noise Removal - if you don't like it, Undo it! |
|||
:* The brain doesn't like Total Silence. Total silence seems to alarm the brain, and that's not a good thing when you're listening to an audiobook for pleasure. It's better to leave a tiny bit of noise than to go for complete and total silence between the words. This helps the brain stay engaged and lends to a smooth enjoyable listening experience! |
|||
{| |
{| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 8: | Line 18: | ||
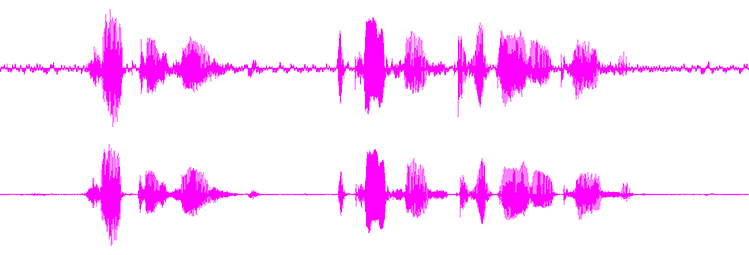
[[Image:goldwave-NC-before-and-after.gif]] |
[[Image:goldwave-NC-before-and-after.gif]] |
||
It is easy to ''over-clean'' for noise. If the settings are too high, the noise cleaning will be too aggressive, and the result is that there is distortion to the voice and artifact left in the recording that detracts for the listener's pleasure. In general, it is better to leave a tiny bit of noise in the space between the words rather than try to create total silence in the space between the words. The brain reacts by being startled when confronted with total silence. If there is a ''tiny'' bit of noise, the brain remains engaged, and the listener's pleasure is not disrupted. |
|||
| ⚫ | Here is a funny collection of [http://www.pdsounds.org/audio/download/89/your_noise.mp3 noises found in |
||
| ⚫ | Here is a funny collection of [http://www.pdsounds.org/audio/download/89/your_noise.mp3 noises found in Librivox recordings]. Of course, ''any'' Noise Removal software would fail on monster noises such as these, and would result in these well known whirling and ringing, Darth Vader-like voices. But, thankfully, in the vast majority of Librivox recordings Noise Removal can be done with minimal to no artifacts and with great effect to overall listening pleasure. ''Find samples below''. And it is free. And not much work. |
||
== |
== Noise Reduction with the free Audacity software == |
||
: ''If you would like to see a tutorial with pictures, please go [[Noisecleaning With Pics|here]].'' |
: ''If you would like to see a tutorial with pictures, please go [[Noisecleaning With Pics|here]].'' |
||
: ''For a very detailed explanation of the sliders and their effects, go [[Detailed Audacity Noise Removal|here]].'' |
: ''For a very detailed explanation of the sliders and their effects, go [[Detailed Audacity Noise Removal|here]].'' |
||
Audacity is the audio recorder and editor of choice for most Librivox volunteers. It's free and very good considering that it is free |
Audacity is the audio recorder and editor of choice for most Librivox volunteers. It's free and very good, especially considering that it is free. |
||
<div class="note"> |
|||
'''Audacity 1.3.3 beta - [http://audacity.sourceforge.net/ Download]''' |
|||
Although Audacity does a great job at removing noise, it remains very important to prevent as much noise as possible from being recorded in the first place. Measures should be taken to record in quiet, insulated environments, away from other electrical devices and circuitry! </div> |
|||
'''Audacity - [http://web.audacityteam.org/download/ Audacity Download Page]''' |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
'''Listen to four noisecleanings done with audacity'''<br> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
<div class="note"> |
<div class="note"> |
||
Note: If your noise-pattern changes over time of the complete recording (which is the worst case scenario), you'll have to split the noise reduction task into several goes. First third, middle, last third...or something. Each time sampling a piece of noise from that part and then selecting only that part to apply the |
Note: If your noise-pattern changes over time of the complete recording (which is the worst case scenario), you'll have to split the noise reduction task into several goes. First third, middle, last third...or something. Each time sampling a piece of noise from that part and then selecting only that part to apply the noise reduction to. |
||
</div> |
</div> |
||
== Noise Reduction with free Audacity 2.1.0 and later versions == |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
The method of noise-cleaning has changed radically in version 2.1.0. For a technical explanation see [http://wiki.audacityteam.org/wiki/How_Audacity_Noise_Reduction_Works#algorithm How Audacity Noise Reduction Works] in the Audacity Wiki. |
|||
* '''Find a piece of PURE(!) background noise in your recording.''' Click and drag to select the noise. No mouseclicks in it. No breathing in it...pure dead air. Mostly you can find this at the end of your recording. Zoom in to see it easier. The longer the better. [The audio term for this is "room tone." Tip: When you want to blank something out on your recording, or add a little pause, use roomtone rather than silence.] |
|||
If your problem is mains hum or constant whistle, the use of a Notch Filter may help. This should be done ''before'' applying Noise Reduction. See [http://wiki.librivox.org/index.php/Removing_Mains_Hum Removing Mains Hum] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* Change the audacity preferences to increase the amount of seconds the preview will run - hit '''CTRL-P''' Change it from 3 seconds to 10 or so. (When you use "preview" below, you'll be able to hear this much from the beginning of your file.) |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* Lower all sliders to a low position. Set '''attack/decay time''' to 0.01 and hit '''preview ''' |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* Increase the second slider in small steps and preview again and again until you are satisfied with the preview. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* Select a piece of background noise (no speech, breaths or other noises) in your audio. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
<div class="note">I learned from Durin Gleaves of Adobe that the "Soundbooth beta will remain active into August, but will expire at that time."</div> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* Set all sliders to 6. Hit '''Preview '''. |
|||
* The most likely setting for '''Sensitivity''' (second slider) will be 6. If you have very light noise, you may try a lower setting. If you can still hear noise behind your voice, increase the slider. |
|||
* The most likely setting for the '''Frequency Smoothing (bands)''' (third slider) is 6. This equates to the 150Hz Frequency Smoothing in previous versions of Audacity (see above). |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
** A setting of 6 would be very light noise removal - use if you have very little noise |
|||
** A setting of 12 would be a moderate setting - use if you have moderate noise |
|||
** A setting of 18 would be a stronger setting - use if you have a nuisance noise, but consider also whether you should have used a Notch Filter before using Noise Reduction (see above). Leaving a little background ambience is definitely preferable to introducing unwanted 'artifacts' and distortions by cleaning too heavily. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Further explanations and advice may be found at [http://manual.audacityteam.org/o/man/noise_reduction.html Noise Reduction] in the Audacity Wiki. |
|||
| ⚫ | <div class="note">Note: If your noise-pattern changes over time of the complete recording (which is the worst case scenario), you'll have to split the noise reduction task into several goes. First third, middle, last third...or something. Each time sampling a piece of noise from that part and then selecting only that part to apply the |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Development and sales of Adobe Soundbooth ended on April 11, 2011. Soundbooth users can apparently take advantage of a "special upgrade" offer to Adobe Audition. I do not know if the instructions below are still correct. If anyone who uses Soundbooth can check and correct them, please PM RuthieG. |
|||
Adobe Soundbooth is part of the brand new Adobe Creative Suite 3 (as of May2007). Adobe, on their own website, handed out a [http://labs.adobe.com/technologies/soundbooth/ soundbooth beta version] '''for free'''. That's a 200$ product you can use for free. All the functions you need for Librivox are working - With ONE exception - It only handles wav files and no mp3 files. For Windows and Mac (Intel Macs only). System requirements: http://labs.adobe.com/technologies/soundbooth/#sysreqs |
|||
If you don't like to register at Adobe you can also download it from [http://www.pdsounds.org/files/librivox_temp/AdobeSoundbooth_Beta.rar here]. |
|||
| ⚫ | Soundbooth's handling is very "visual" and "what you see is what you get" oriented. Soundbooth features an '''astonishing |
||
| ⚫ | <div class="note">Note: If your noise-pattern changes over time of the complete recording (which is the worst case scenario), you'll have to split the noise reduction task into several goes. First third, middle, last third...or something. Each time sampling a piece of noise from that part and then selecting only that part to apply the noise reduction to.</div> |
||
'''[http://www.moebius.mynetcologne.de/librivox/utopia_sweetening.mp3 Here is a Before:After sample]''' (also used the soundbooth equalizer) |
|||
| ⚫ | Soundbooth's handling is very "visual" and "what you see is what you get" oriented. Soundbooth features an '''astonishing noise reduction filter''' which cannot be imagined any easier to use but yields great results. Soundbooth also features a priceless '''spectral waveform display''', which comes in very handy if you get a little deeper into audio restoration. |
||
=== 1. Select a piece of noise in your audio === |
=== 1. Select a piece of noise in your audio === |
||
* ''' Click and drag to select a piece of PURE(!) noise.''' No |
* ''' Click and drag to select a piece of PURE(!) noise.''' No mouse clicks in it. No inhaling in it. No car coming up the driveway...pure dead air. |
||
* '''In Menu click: Tasks > Clean Up Audio ''' |
* '''In Menu click: Tasks > Clean Up Audio ''' |
||
* '''in the left panel click button: Capture Noiseprint''' |
* '''in the left panel click button: Capture Noiseprint''' |
||
* '''Press CTRL-A''' to select your complete recording |
* '''Press CTRL-A''' to select your complete recording |
||
=== 2. |
=== 2. Noise reduction === |
||
* '''In the left panel click button: Noise''' |
* '''In the left panel click button: Noise''' |
||
* '''Check the "use Captured Noise print" box''' |
* '''Check the "use Captured Noise print" box''' |
||
| Line 71: | Line 90: | ||
* '''To finetune the result''' play again with upper Reduction slider values between 60-100% and a little bit with the Reduce-By slider. |
* '''To finetune the result''' play again with upper Reduction slider values between 60-100% and a little bit with the Reduce-By slider. |
||
== |
== Noise cleaning with Goldwave == |
||
Goldwave is a wonderfully fast |
Goldwave is a wonderfully fast all-round sound editor for all your audio needs - '''it is not free, yet very cheap for what it can do'''. |
||
| ⚫ | <div class="note">Note: If your noise-pattern changes over time of the complete recording (which is the worst case scenario), you'll have to split the noise reduction task into several goes. First third, middle, last third...or something. Each time sampling a piece of noise from that part and then selecting only that part to apply the noise reduction to.</div> |
||
'''[http://www.moebius.mynetcologne.de/librivox/counterpane_NC_goldave_before_and_after.mp3 Here is a Before:After sample]''' |
|||
| ⚫ | <div class="note">Note: If your noise-pattern changes over time of the complete recording (which is the worst case scenario), you'll have to split the noise reduction task into several goes. First third, middle, last third...or something. Each time sampling a piece of noise from that part and then selecting only that part to apply the |
||
=== 1. Select a piece of noise in your audio === |
=== 1. Select a piece of noise in your audio === |
||
Use the left and right mouse button to mark start and end of a selection with PURE(!) noise in it. |
Use the left and right mouse button to mark start and end of a selection with PURE(!) noise in it. |
||
No |
No mouse clicks in it. No inhaling in it. No car coming up the driveway...pure dead air. Copy this to Clipboard with CRTL-C. |
||
Now press CTRL-A to select all of your recording. |
Now press CTRL-A to select all of your recording. |
||
| Line 92: | Line 109: | ||
* '''Overlap to 95%''' |
* '''Overlap to 95%''' |
||
* '''Scale 70'''. (play between 60-100)(keep some bearable noise in. Keep some very light *tinkeling* in too, we will remove it in the next step) |
* '''Scale 70'''. (play between 60-100)(keep some bearable noise in. Keep some very light *tinkeling* in too, we will remove it in the next step) |
||
* '''Save settings to a preset:''' " |
* '''Save settings to a preset:''' "LibriVox Speech" |
||
| Line 105: | Line 122: | ||
* '''Release (s): 1.000''' |
* '''Release (s): 1.000''' |
||
* '''Save settings to a preset:''' "Kill mini noises" |
* '''Save settings to a preset:''' "Kill mini noises" |
||
== Noisecleaning with Apple's GarageBand == |
|||
{| border="1" |
|||
|- |
|||
|Details forthcoming |
|||
|- |
|||
|} |
|||
Similar techniques can be used in Audacity, within Audacity's limitations, if the Apple FX is available. |
|||
Latest revision as of 12:23, 14 October 2022
Before Noisecleaning
Before doing any processing on your file, do export a copy of your file in FLAC format (click File | Export Audio and select FLAC files from the 'Save as type' drop-down menu). Then if anything goes wrong, you have a raw lossless copy that you can import back into Audacity.
Noisecleaning
In Librivox files, Noise Removal works by removing or reducing the amount of "noise" between the speaking portions of our recordings. Whichever program is being used, the concept is the same. The program must be told what the "noise" is to be defined as (that's your job), and then the program diminishes the "noise" that it finds within the file, to the degree that you tell it to do so. You can change the settings so that the program diminishes the noise very aggressively, or very lightly.
There are some simple but important points to remember before you start Noise Removal.
- Leave some "room silence" at the end of your recording where everything is as quiet as possible. This is what you will use to tell the program what "noise" is.
- It's better to run light Noise Removal twice than to do it aggressively once.
- Always listen to the file after you've done the Noise Removal - if you don't like it, Undo it!
- The brain doesn't like Total Silence. Total silence seems to alarm the brain, and that's not a good thing when you're listening to an audiobook for pleasure. It's better to leave a tiny bit of noise than to go for complete and total silence between the words. This helps the brain stay engaged and lends to a smooth enjoyable listening experience!
| Golden Rule: Always do noisecleaning with headphones! |
| Silver Rule: Rather leave some noise in your recording, than to garble it with over-cleaning and ringing artifacts. |
It is easy to over-clean for noise. If the settings are too high, the noise cleaning will be too aggressive, and the result is that there is distortion to the voice and artifact left in the recording that detracts for the listener's pleasure. In general, it is better to leave a tiny bit of noise in the space between the words rather than try to create total silence in the space between the words. The brain reacts by being startled when confronted with total silence. If there is a tiny bit of noise, the brain remains engaged, and the listener's pleasure is not disrupted.
Here is a funny collection of noises found in Librivox recordings. Of course, any Noise Removal software would fail on monster noises such as these, and would result in these well known whirling and ringing, Darth Vader-like voices. But, thankfully, in the vast majority of Librivox recordings Noise Removal can be done with minimal to no artifacts and with great effect to overall listening pleasure. Find samples below. And it is free. And not much work.
Noise Reduction with the free Audacity software
- If you would like to see a tutorial with pictures, please go here.
- For a very detailed explanation of the sliders and their effects, go here.
Audacity is the audio recorder and editor of choice for most Librivox volunteers. It's free and very good, especially considering that it is free.
Audacity - Audacity Download Page
As for any noise cleaning software: The harder the noise the more difficult it is to noise clean it without drawbacks. Audacity copes well. And it's free!
Note: If your noise-pattern changes over time of the complete recording (which is the worst case scenario), you'll have to split the noise reduction task into several goes. First third, middle, last third...or something. Each time sampling a piece of noise from that part and then selecting only that part to apply the noise reduction to.
Noise Reduction with free Audacity 2.1.0 and later versions
The method of noise-cleaning has changed radically in version 2.1.0. For a technical explanation see How Audacity Noise Reduction Works in the Audacity Wiki.
If your problem is mains hum or constant whistle, the use of a Notch Filter may help. This should be done before applying Noise Reduction. See Removing Mains Hum
Step 1 - Select a piece of background noise
- Select a piece of background noise (no speech, breaths or other noises) in your audio.
- In Menu click: Effect > Noise Reduction... A dialog will pop up.
- Click "Get Noise Profile" The dialog box will close instantly.
Step 2 - Noise Reduction
- Press CTRL-A / Command-A to select your complete recording.
- In Menu click: Effect > Noise Reduction... again. Note: don't select "Repeat Noise Reduction" -- that instantly applies the default settings; you want to adjust the settings and preview the results before you apply the noise filters.
- Set all sliders to 6. Hit Preview .
- The most likely setting for Sensitivity (second slider) will be 6. If you have very light noise, you may try a lower setting. If you can still hear noise behind your voice, increase the slider.
- The most likely setting for the Frequency Smoothing (bands) (third slider) is 6. This equates to the 150Hz Frequency Smoothing in previous versions of Audacity (see above).
- Now experiment with the Noise Reduction slider (first slider) and increase it in small steps and preview again and again until you are satisfied with the preview.
- A setting of 6 would be very light noise removal - use if you have very little noise
- A setting of 12 would be a moderate setting - use if you have moderate noise
- A setting of 18 would be a stronger setting - use if you have a nuisance noise, but consider also whether you should have used a Notch Filter before using Noise Reduction (see above). Leaving a little background ambience is definitely preferable to introducing unwanted 'artifacts' and distortions by cleaning too heavily.
- Make sure that the 'Reduce' radio button is checked, and hit OK ~- (the effect may take a couple of minutes if it is a long file) -~ Done!
Further explanations and advice may be found at Noise Reduction in the Audacity Wiki.
Noisecleaning with Adobe Soundbooth
Development and sales of Adobe Soundbooth ended on April 11, 2011. Soundbooth users can apparently take advantage of a "special upgrade" offer to Adobe Audition. I do not know if the instructions below are still correct. If anyone who uses Soundbooth can check and correct them, please PM RuthieG.
Soundbooth's handling is very "visual" and "what you see is what you get" oriented. Soundbooth features an astonishing noise reduction filter which cannot be imagined any easier to use but yields great results. Soundbooth also features a priceless spectral waveform display, which comes in very handy if you get a little deeper into audio restoration.
1. Select a piece of noise in your audio
- Click and drag to select a piece of PURE(!) noise. No mouse clicks in it. No inhaling in it. No car coming up the driveway...pure dead air.
- In Menu click: Tasks > Clean Up Audio
- in the left panel click button: Capture Noiseprint
- Press CTRL-A to select your complete recording
2. Noise reduction
- In the left panel click button: Noise
- Check the "use Captured Noise print" box
- Set Reduction slider to 100%
- Now Play with the Reduce-By slider starting very left ( 0db)and setting it higher and listen until perhaps (16db) or until you are satisfied with the results.
- To finetune the result play again with upper Reduction slider values between 60-100% and a little bit with the Reduce-By slider.
Noise cleaning with Goldwave
Goldwave is a wonderfully fast all-round sound editor for all your audio needs - it is not free, yet very cheap for what it can do.
1. Select a piece of noise in your audio
Use the left and right mouse button to mark start and end of a selection with PURE(!) noise in it. No mouse clicks in it. No inhaling in it. No car coming up the driveway...pure dead air. Copy this to Clipboard with CRTL-C.
Now press CTRL-A to select all of your recording.
2. Noise reduction
- In Menu click: Effect > Filter > Noisereduction
- Set to "use clipboard"
- Set FFT to 12 (try 11 or 12) (10 and 13 won't work)
- Overlap to 95%
- Scale 70. (play between 60-100)(keep some bearable noise in. Keep some very light *tinkeling* in too, we will remove it in the next step)
- Save settings to a preset: "LibriVox Speech"
3. Killing remaining noises with a Compressor/Expander
We want remaining low volume sounds to be removed in between pauses.
- In Menu click: Effect > Compressor/expander
- Set mode: Expander
- Settings: Check Anticipate Attack; Check Use smoother
- Multiplier (db): -15.0
- Threshold (db): -53.0 (play with -56 to 45)
- Attack (s): 0.015
- Release (s): 1.000
- Save settings to a preset: "Kill mini noises"